The code for this Angular Typeahead is on my GitHub:
JeffreyBane/ALF-My-TypeAhead-App (github.com)
I know what you’re thinking. “I want to have a sexy looking web form with a sweet Angular Typeahead component so all the women and or men will want me.” So, spoiler – nobody is going to be more attracted to you because you’ve implemented a Typeahead search. BUT it will give your users a much more satisfying usability experience in your app.
That’s kind of the same! (That’s not the same at all.)
So, let’s continue our never-ending quest to understand all the higher order mapping operators by coding a Typeahead search. We’ve used concatMap on multiple occasions, in Avoiding Nested Subscriptions in Angular and also Populating Multiple Dropdowns in Angular Using forkJoin. Today we’ll be letting switchMap show its stuff and why it’s so useful in a situation like this – where the user will be changing their search term frequently, essentially every time they are done typing.
So, let’s jump right in. First thing we’ll need is Angular Material. We’ll be using the material autocomplete form control for our Typeahead. It takes care a lot of the details for us so it’s ideal for this example. Plus it looks sexy. (Again, the woman and or men are NOT going to want you for implementing a Typeahead in your code – I can’t stress this enough.)
We install Angular Material like so:
>> ng add @angular/materialI go into Angular Material in a bit more detail in this article Displaying a Loading Dialog on an Angular Parent Component While Child Components Load, but for now, just select yes to everything and pick a color theme. I’m going to get nutty and select Deep Purple/Amber for our example, but you pick whatever you want.
Let’s modify our app module to import the Angular Material items we need. Let’s also add Forms and Reactive Forms as we’ll use those later as well. Add these imports and also add them to the imports array:
App Module (app.module.ts)
import { FormsModule, ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { MatFormFieldModule } from "@angular/material/form-field";
import { MatInputModule } from '@angular/material/input';
import { MatAutocompleteModule } from '@angular/material/autocomplete';
.....
imports: [
BrowserModule,
AppRoutingModule,
BrowserAnimationsModule,
FormsModule,
ReactiveFormsModule,
MatFormFieldModule,
MatInputModule,
MatAutocompleteModule
],Now let’s start on our app. We’re going to create a system whereby new superheroes in the Marvel universe can see what superhero names are still available. (There’s not many after 15 years.) Once they select an available name from our Typeahead, they’ll be directed to a detail page where they can see more information about the name, how much it costs, their origin story, what superpowers they will gain, etc.
I’m fairly certain this is not how new superheroes come about. But let’s get going!
To start, we’ll create a service to return the available superhero names for our users to choose from. In the real world, this would obviously be a database operation where our API would submit a query to our backend to retrieve the list of names and eventually detail information. However, in this article we’re just going to focus on the Typeahead, so in our service we’ll simply return a JSON object array. We’ll also filter that array on items that contain any of the characters in the search term the user has entered.
Let’s create that very service:
>> ng g s type-aheadAnd the contents:
Typeahead service (type-ahead.service.ts)
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Observable, of } from 'rxjs';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class TypeAheadService {
getDropDownData(searchValue: string): Observable<any[]> {
const mockJson = [
{ id: '1', value: 'The Visible Girl', disabled: false },
{ id: '2', value: 'Anxiety Man', disabled: false },
{ id: '3', value: 'Acne Boy', disabled: false },
{ id: '4', value: 'The Human Goiter', disabled: false },
{ id: '5', value: 'Vegan Zombie', disabled: false },
{ id: '6', value: 'Windows Update', disabled: false },
{ id: '7', value: 'JavaScript Diaper', disabled: false },
{ id: '8', value: 'The Incredible Middle Manager', disabled: false },
{ id: '9', value: 'Commander Reflux', disabled: false },
{ id: '10', value: 'Urinal Mint', disabled: false },
{ id: '11', value: 'Pause Squat', disabled: false },
{ id: '12', value: 'The Turd', disabled: false },
{ id: '13', value: 'Extended Warranty', disabled: false }
];
return of(mockJson.filter(item =>
item.value.toLowerCase().indexOf(searchValue.toLowerCase()) > -1));
}
}
So again, this would be a database call in a real app, and the filtering would occur there, but for our example we’re just going to return the list of available names and filter on the variable “searchValue” passed to our service method getDropDownData. Note each item has a value of “disabled: false” added to it. You’ll see why in a bit.
Our app also is going to have a search form and a detail form as the landing page once a search item is selected in our Typeahead. We’ll use Angular Routing and set up our app component form with pretty much nothing but some text and a router outlet:
App component (app.component.html)
<h1>The Big List of MCU Unused Superhero Names.</h1>
<h2>Please Select Your New Identity!</h2>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>Now let’s create our 2 components, the search and detail:
>> ng g c type-ahead
>> ng g c detail-pageAnd then one last item before the fun begins, let’s add our routing with a default route of our Typeahead search component:
App routing module (app-routing.module.ts)
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { DetailPageComponent } from './detail-page/detail-page.component';
import { TypeAheadComponent } from './type-ahead/type-ahead.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'TypeAhead',
component: TypeAheadComponent
},
{
path: 'DetailPage',
component: DetailPageComponent
},
{ path: '',
redirectTo: '/TypeAhead',
pathMatch: 'full' },
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }Fabulous, let’s get Typeaheading! (That’s not a word.) We’ll go ahead and enter the guts of our Typeahead form, then we’ll talk about it bit by bit:
Typeahead form (type-ahead.component.html)
<div>
<form>
<mat-form-field style="margin-left: 20px; width: 300px;">
<mat-placeholder>Type some characters, future hero</mat-placeholder>
<input matInput [formControl]="searchBox" [matAutocomplete]="ac" id="searchBox" />
<mat-autocomplete #ac="matAutocomplete" (optionSelected)="itemSelected($event)">
<mat-option *ngFor="let option of searchResults; " [disabled]="option.disabled" [value]="option.id">
{{ option.value }}
</mat-option>
</mat-autocomplete>
</mat-form-field>
</form>
</div>So let’s look at the 2 main parts of our form. First we’re wiring up a mat-form-field wrapper for everything. The first item within is a placeholder, which just looks impressive, and also gives some rudimentary instruction, in this case “Type some characters, future hero”
<mat-form-field style="margin-left: 20px; width: 300px;">
<mat-placeholder>Type some characters, future hero</mat-placeholder>Next the actual matInput for our textbox to type in:
<input matInput [formControl]="searchBox" [matAutocomplete]="ac" id="searchBox" />We also wire our input up to a formControl in the code behind called “searchBox”, so we can access it programmatically. Finally we wire up this input to our auto complete element which we’ll discuss next. This is done by setting the [matAutoComplete] property of the matInput to a template reference of “ac” (though you could use any name):
[matAutocomplete]="ac"This is the template reference we’ll specify on our autocomplete so the two can interact. And that brings us to our Angular Material auto complete item:
<mat-autocomplete #ac="matAutocomplete" (optionSelected)="itemSelected($event)">
<mat-option *ngFor="let option of searchResults; " [disabled]="option.disabled" [value]="option.id">
{{ option.value }}
</mat-option>
</mat-autocomplete>As stated, we’ll assign the autocomplete a template reference of “#ac” so our input can talk to it. We’ve also got a method tied to the optionSelected event of the auto complete. This fires, (you guessed it future hero!) when one of the autocomplete items is clicked on. That’s where we’ll determine what item was selected and route to our detail form. The remainder is a pretty typical ngFor, which will loop through each item of our searchResults array and bind them to the autocomplete. However, do note we’re also setting the disabled attribute of each item to the disabled property of each object in our JSON array. Again, you’ll see why this is when we get into the code behind, but every item from our service has “disable = false”, so they are all selectable.
Let’s see what the fruit of our thus far labor looks like. In order to get this code to compile, temporarily add these 3 items to the component class in the typescript file.
Typeahead component (type-ahead.component.ts)
export class TypeAheadComponent implements OnInit {
public searchBox = new FormControl();
public searchResults: any[] = [];
itemSelected(event): void {
}We’ll delete all that in a minute, but now our code will run, and you can see what our form looks like in all its glory, albeit with no items being returned when we type:

You can see the placeholder already knows how to behave and gives a very nice effect when we click in the input and type something. Go ahead and delete the items we temporarily put into the component, and we’ll start building the real component.ts file a piece at a time. Let’s start with all the class variables we’ll need:
Typeahead component (type-ahead.component.ts)
export class TypeAheadComponent implements OnInit {
public searchBox = new FormControl();
public clearedBox = true;
public searchTerm = '';
// Object bound to autocomplete
public searchResults: any[] = [];
// Empty default object for when the search box doesn't have anything in it
public defaultResults: any[] = [];
// JSON to display when no items are returned from the service
public noResult: any = {
id: 0,
value: 'No names match criteria',
disabled: true
};
public noResults: any[] = [];We start by declaring our FormControl called searchBox which is the input on our form. Then we create a Boolean called clearedBox (more on that in a bit) and a string to hold our searchTerm called, um, searchTerm (duh.) Next searchResults is the array that is bound to our autocomplete and will be assigned the values returned from our service. We then set up 2 more arrays:
- defaultResults which is an empty array we use to initilze the list to nothing.
- noResults which is what we want to display if the user types something that has NO match in our list. (Note disabled is set to true for this item. Again you’ll see why in a minute.)
We’ll pass 2 services into the constructor, the router service and of course our Typeahead service:
constructor(
private _TypeAheadService: TypeAheadService,
private _router: Router
) { }Now onto the ngOnInit method and all the nougaty goodness that makes this form work. Here’s the entire ngOnInit – we’ll break it down bit by bit after:
ngOnInit(): void {
// Add our not found item to the noResults array
this.noResults[0] = this.noResult;
// set the inital value of searchResults to our empty array
this.searchResults = this.defaultResults;
// Setup a debounce time constant of 1/2 a second.
const DEBOUNCE_TIME = 500;
// get values from the service
this.searchBox.valueChanges.pipe(
debounceTime(DEBOUNCE_TIME),
switchMap(changedValue => {
if (changedValue.trim() !== '') {
this.searchTerm = changedValue.trim();
this.clearedBox = false;
return this._TypeAheadService.getDropDownData(this.searchTerm);
} else {
this.searchTerm = '';
this.clearedBox = true;
return of(this.defaultResults);
}
}
)
).subscribe(data => {
if (data.length === 0) {
if (this.clearedBox) {
this.searchResults = data;
} else {
this.searchResults = this.noResults;
}
} else {
this.searchResults = data;
}
}
);
}Before we call our service, we do some simple things like adding our noResult object to the noResult array, set searchResults to defaultResults (blank) and also setup a constant for debounce time. (I put the constant definition right above the service call for readability, you’d put it in the class variables normally).
And now the actual subscription. We’re going to subscribe to an event called valueChanges of our searchBox control. In Angular, FormControls (and some other form objects) have a really useful event exposed called valueChanges. valueChanges is an observable that we can subscribe to so that each time the value of the textbox changes we can do stuff, in this case, filter our autocomplete list of items.
Starting with valueChanges, we pipe the results:
this.searchBox.valueChanges.pipe(We pipe the results to the debounceTime operator. This guy is a lifesaver. It allows you to wait a certain amount of time before emitting. In our case we set this to a half a second, using our constant:
debounceTime(DEBOUNCE_TIME),Now if the user fires valueChanges again (i.e., types something else within half a second), the timer is reset and the half a second count begins again. Why do we do this? Well imagine if we didn’t do this – Our autocomplete would fire off populating a new list after every character entered, as the user types. If there were a delay in the results being returned as would be typical in a real-world app, we’d be firing off API calls left and right before any of them had a chance to return results, putting more stress on the backend / db than needs be. By using debounce, we create a magical, pleasant experience where the webform essentially says to the user – “Ok, are you done typing? Since it’s been half a second, I think you are, and I’ll go populate the autocomplete list now. Also have a great day!”
Now we need to emit this value (what the user has typed) to a new observable. We do this using a higher order mapping operator. In our case switchMap is going to work great with our Typeahead. switchMap unsubscribes from any prior inner Observable and subscribes to any new inner Observable. This has the very desirable effect of stopping any prior inner Observable before processing the new one, exactly what we want in this case. In other words, if switchMap could speak English it would say something like – “Hey, we got a new value emitted here, whatever you were doing – just throw it out the window and process this new value. Also, have a great day!” (Our sentient code creatures are apparently very polite.)
switchMap(changedValue => {We’ve called our debounced value “changedValue” and we’ll just simply check that the change wasn’t the user clearing the textbox out. Also, If the user cleared out the text or typed something that had no matches, we’ll handle all that shortly.
if (changedValue.trim() !== '') {Passing that check, we know the user actually did type something, so let’s do a few things. First, we’ll trim the value:
this.searchTerm = changedValue.trim();Next we’ll set the variable we have called “clearedBox” to false. We use this Boolean to indicate if the user cleared out the text box or not and handle that in the subscribe. Since we checked for a value above in our if, we know this is false and the user hasn’t cleared the textbox:
this.clearedBox = false;Finally we pass the search term to the service and return the Observable to our subscribe:
return this._TypeAheadService.getDropDownData(this.searchTerm);Otherwise (else), the user did indeed clear the box. In that case, we set searchTerm to “”, set clearedBox to true, and return an Observable of defaultResults which again we simply defined earlier as an empty array:
} else {
this.searchTerm = '';
this.clearedBox = true;
return of(this.defaultResults);
}Finally, the subscribe:
).subscribe(data => {So, we’ve called our service and MAYBE gotten some data back, we don’t know yet – the user could have typed complete gibberish into the search box, or some characters that don’t match any name in our list. So let’s check if the service returned any values:
if (data.length === 0) {Now you’ll see what “clearedBox” is used for. Recall a bit back, prior to our subscribe, we’re returning one of 2 observables. Either the result set from our service (if the user actually typed something) or our default result (if the user cleared out the textbox). If the latter, we also set clearedBox to true. Thanks to that good work, when we subscribe, we will now automatically get the appropriate observable plus we’ll know if the user cleared the textbox. So all we really need to check for now is did the service return any data, i.e., is the length 0 or not. The reason being- we want to differentiate if the service returned no rows (the user typed something that didn’t return any names) or the user cleared the textbox. If we set clearedBox to true earlier, the user indeed cleared the checkbox, and we simply display the defaultResults we are returning automatically in the observable. If clearedBox is false and the service data.length = 0, we know the service didn’t return any matching rows. In that case, we want to display the noResults array (the message saying, “No names matched”.) This way we’re not telling them the service returned no results if they cleared the textbox, which would be annoying. So if they cleared the textbox, display the observable, otherwise display the noResults message:
if (this.clearedBox) {
this.searchResults = data;
} else {
this.searchResults = this.noResults;
}Else (if we have a data.length that doesn’t equal 0) the user typed a search term that had some matches, the service indeed returned some data and that’s what we’ll display in the Material autocomplete:
} else {
this.searchResults = data;
}
}Now the data our autocomplete display is all taken care of, for the last bit of our component, we’ll handle the itemSelected event and route to our detail page, passing along the id of the selected item, utilizing the state navigation option.
itemSelected(event): void {
this._router.navigate(['/DetailPage'], { state: { selectedId: event.option.value } });
}Ok. Let’s have a look at all this working! But first let’s code up our simplified detail component as that’s the final piece we’ll need. The component code:
Detail component (detail-page.component.ts)
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'app-detail-page',
templateUrl: './detail-page.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./detail-page.component.scss']
})
export class DetailPageComponent implements OnInit {
selectedId: number;
constructor(private _router: Router) {
this.selectedId = this._router.getCurrentNavigation().extras.state.selectedId;
}
ngOnInit(): void {
}
}
In our itemSelected() event handler in the Typeahead form, we passed along the option value that was selected using a variable we called selectedId.
Our detail page does nothing more than grab this variable from the navigation state and assign it to a local variable of the same name, selectedId. In a real-world app, you’d take this primary key, and run a query to return detail information of the item they selected. In our unused superhero name app, we’d requery the database to get all the specifics on the name they selected, such as what superpowers it comes along with, their origin story, pricing, etc. and ultimately a way to purchase the name. But again, that’s beyond the scope of the Typeahead that’s being demonstrated in this article, so our detail form will simply display the key of the item selected:
Detail form (detail-page.component.html)
<h3>You selected the item with id of {{ selectedId }} !!</h3>And with that, our unused MCU superhero name generator lookup thingy is ready to roll! Let’s fire off the app and see how everything functions. Start the app and type the word “the” into our input:
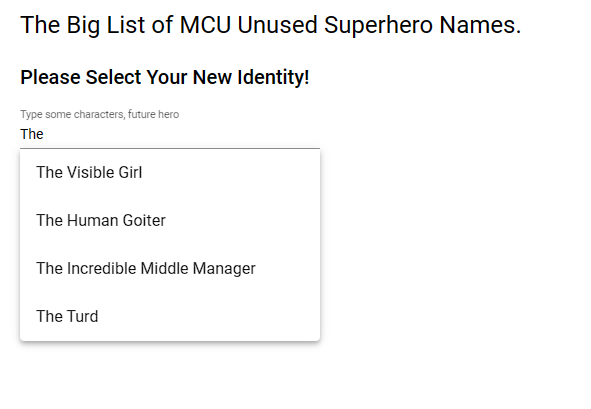
Excellent – you can see the values are filtered on anything that contains the word “the”. Notice how the debounce of 1/2 second is also working. If you type “the” one letter at a time very slowly, you can see the list is refreshed for every letter you type. But if you type “the” somewhat quicker, the debounce ensures that the list is only retrieved when you are done typing. (haven’t touched a key for the 1/2 second, firing the valueChanges() event.) Debounce makes for a pleasant UX experience and prevents our API from getting called more than necessary. Win / win for all.
Back in our app, go ahead and select “The Incredible Middle Manager” (No doubt his superpowers would include scheduling meetings and micromanaging in a single bound):

And voila, we have the primary key (id) of the item selected in the previous form by our Typeahead! Let’s do a few more things to see some of the remaining functionality we coded. First off, return to the type ahead form and type some gibberish, “xyz” or anything that won’t return any results:
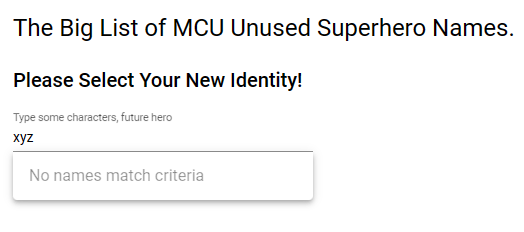
Remember how we set disabled: true on our no results item? Now you can see why – the user gets a message that states nothing was found for that search string, but it’s not something they can select. There’s a couple of ways to handle a no results message, but I like this way for a few reasons. First, it’s not a lot of code and second, the message shows up in the autocomplete, exactly where the user expects their results to show up. If we put “No names found” in a separate label somewhere else on the screen, it would be a bit jarring, and I like consistency. So with the simple addition of “disabled” true or false to each item, we can display whatever we want in the results AND prevent the user from clicking on informational messages. But feel free to handle this message differently if you care to. Finally, go ahead and clear out what you typed in the box:

Notice how we don’t get the “No names found” message any longer. We wouldn’t want to tell the user nothing was found every time they deleted the text from the input. Our user might start screaming uncontrollably “Duh, I haven’t typed anything yet!” and perhaps throwing office furniture, which would suck.
Note: If you grab this code from my GitHub, I’ve included comments in the Typeahead component as to where you would open and close a loading dialog so the user would get a “Please wait…” type message while the data is retrieved:
switchMap(changedValue => {
// Close Loading Panel
if (changedValue.trim() !== '') {
this.searchTerm = changedValue.trim();
// Open Loading PanelWe had no need for these dialogs with our no latency app and they are outside the scope of the article but have a read here Displaying a Loading Dialog on an Angular Parent Component While Child Components Load for all the loading dialog goodness you can handle.
For your reading pleasure:
Higher Order Observables (switchMap at the bottom)
https://blogs.msmvps.com/deborahk/higher-order-observable/
Navigation Behavior Options (state) https://angular.io/api/router/NavigationBehaviorOptions#state
Our good friend debounce
https://rxjs.dev/api/operators/debounce








